PRECLINICAL ASSAYS
Optimize the design of potential future clinical studies with our range of ready-to-use efflux transporter kits.
REQUEST MORE INFO
Assays recommended according to main regulatory authorities.
Worldwide shipments at room temperature thanks to our patented technology.
Highly predictive and useful in the in vitro to in vivo progression.
DDI MODELS
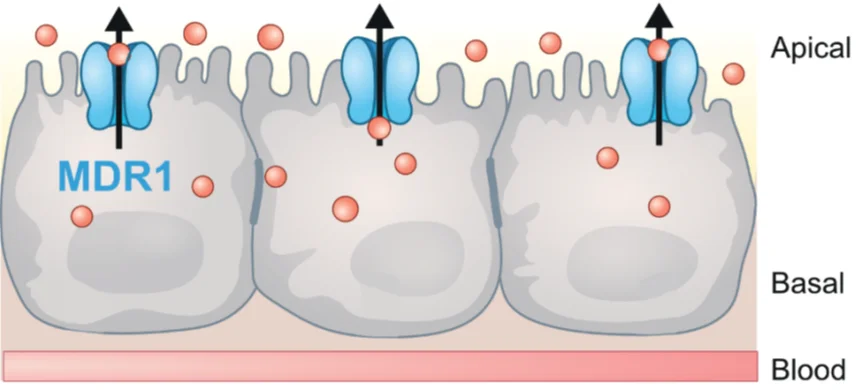
PreadyPort MDR1 is an in vitro model based on Madin-Darby Canine Kidney Type II (MDCKII) cells, genetically modified to express the multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1). This ready-to-use plate is widely used for transport studies to identify drug candidates as substrates of this efflux pump.
MDR1, also known as P-glycoprotein (P-gp), is the most cited drug transporter in pharmaceutical product labelling. Encoded by the ABCB1 gene, this ATP-dependent efflux pump transports a broad range of chemically and structurally unrelated molecules. It plays a crucial role in drug disposition, affecting absorption, distribution, and elimination.
Located in the luminal membrane of several cell types, MDR1 is expressed in key biological barriers, including the intestine, brain, placenta, kidney, and liver, where it contributes to drug-drug interactions and serves as a protective mechanism. By actively pumping potentially toxic compounds out of cells into the blood, bile, or urine, it helps regulate exposure to xenobiotics and endogenous substances.
Regulatory guidelines for drug interaction studies provides recommendations on evaluating transporter-mediated drug-drug interaction studies during the development of a therapeutic molecule.
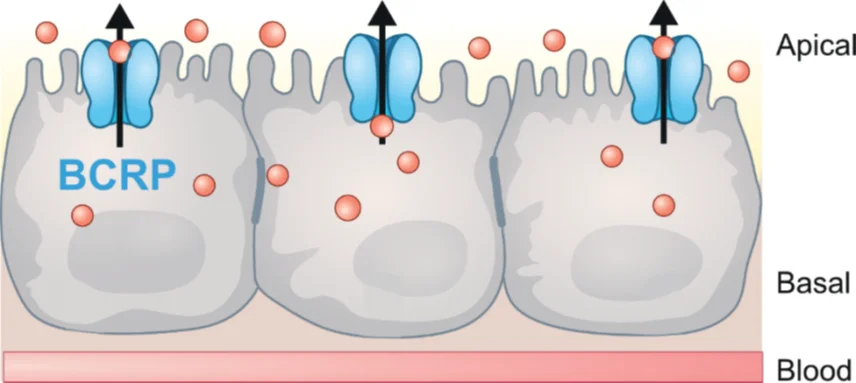
PreadyPort BCRP is an advanced in vitro model based on MDCKII cells genetically modified to overexpress the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) through the ABCG2 gene. This efflux transporter actively moves molecules against a concentration gradient and is widely used to overcome drug resistance in preclinical stages.
BCRP, like MDR1, BCRP, like MDR1, belongs to the ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) transporter family and plays a key role in drug disposition and cellular protection. BCRP is expressed in various tissues, including the testis, placenta, liver, small intestine, and brain.
This efflux transporter, located at the luminal membrane of tissue cell types, recognizes many endogenous and xenobiotic compounds that overlap with MDR1. Beyond this role, BCRP not only participates in drug disposal and its clinical efficacy/toxicity but also maintains cell homeostasis by regulating the transport of endogenous molecules.
Regulatory guidelines for drug interaction studies recommend assessing BCRP-mediated transport for compounds where efflux transporters influence absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME).
Our pre-plated MDCKII cell models overexpress key efflux transporters, such as MDR1 and BCRP, providing a reliable in vitro platform to study drug-drug interactions and transporter-mediated effects.
Screening for transporter interactions is essential for assessing and ranking drug candidates, predicting in vivo drug behavior, and understanding mechanisms influencing drug disposition and efficacy.
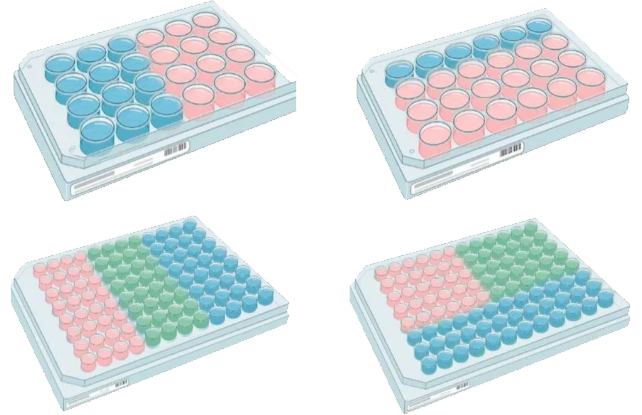
Customize your 24-well and 96-well plates by selecting and combining MDCKII cell clones overexpressing efflux transporters such as MDR1 and BCRP. These flexible assay-ready plates enable the study of drug-drug interactions, transporter selectivity, and efflux mechanisms under your specific experimental conditions.
Understanding the role of efflux transporters is crucial for predicting drug absorption, distribution, and potential drug-drug interactions. These transporters, including MDR1 (P-gp) and BCRP, influence the bioavailability and efficacy of therapeutic compounds.
Dive deeper into efflux transport mechanisms and their impact on drug discovery in our detailed article.
Read more
Evaluation of transporter-mediated drug-drug interaction potential of new molecular entities is mandatory during drug development since these interactions can modify the efficacy and the adverse effects of concomitantly administered drugs.
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) are relevant efflux transporters affecting drug intestinal permeability and brain penetration. In vitro studies of these transporters would also be recommended if biliary excretion or active renal secretion is a major drug elimination pathway.
In addition to regional guidelines, the harmonized guideline for drug interaction studies provides recommendations for designing, conducting, and interpreting these assays.
Some drugs may be potential substrates and inhibitors of efflux transporters.
For example, digoxin and quinidine serve as reference substrates for the multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), while verapamil and valspodar are two well-known inhibitors of this transporter. Likewise, prazosin and dantrolene are substrates of the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), and Ko143 is used as an inhibitor.
Drugs that are substrates for efflux transporters typically exhibit efflux ratios greater than 2 when assessed using bidirectional transport assays across cellular monolayers. The efflux ratio value decreases by at least 50 % in the presence of an inhibitor.
For a more detailed explanation of these reference compounds and their differences, check out our in-depth post on reference compounds.
No, the Shipping Medium consists of a semi-solid culture system specifically designed to preserve cells at room temperature (15-25ºC). This medium maintains a suitable physicochemical environment, keeping adequate moisture conditions for cellular homeostasis and forming a protective cushion that protects cell integrity and functionality during long-distance shipments and up to seven days.
As a general rule, we act as a supplier and do not provide testing services. Nonetheless, feel free to contact us if you wish to test our plates externally. We can direct you to our partners who can assist you in conducting the assay effectively. Additionally, in certain situations, we are open to collaborating to try out new applications of interest to both of us.
Biotechnology company specialized in the development and commercialization of innovative solutions for the pharmaceutical industry and biomedical research.