PRECLINICAL ASSAYS
Improve the efficacy of forthcoming clinical investigations by leveraging our selection of readily-available uptake transporter plates.
Request more information
Full cell functionality after transportation.
Worldwide shipments at room temperature thanks to our patented technology.
Validation data available and high quality-control standards.
DDI MODELS
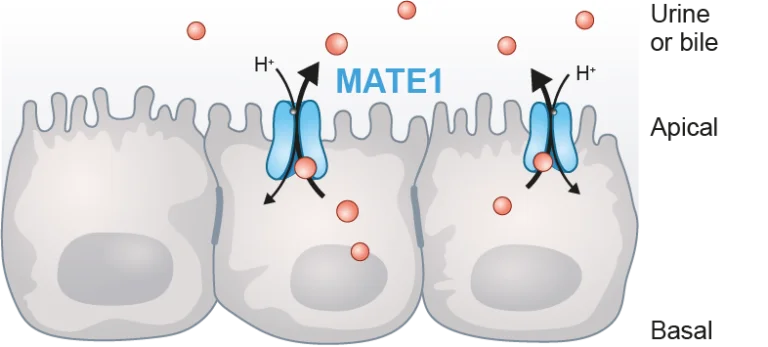
PreadyTake MATE1 contains HEK293 cells transfected with the SLC47A1 gene to overexpress the drug and toxin transporter1 (MATE1). This transporter plays a significant role in the modulation of renal drug elimination and toxicity, and it is closely associated with organic cation transporters (OCTs). Regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of MATE1 for drugs subject to renal secretion.
The MATE1 transporter is part of the solute carrier (SLC) family and is primarily located in the luminal membranes of urinary tubules and bile canaliculi. It plays a crucial role in the renal and biliary elimination of drugs. MATE1 substrates include organic cations such as creatinine, metformin, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), and tetraethylammonium (TEA). The specificity of this transporter for these substrates is similar to that of renal and hepatic organic cation transporters (OCTs).
The pH influences the transport direction of MATE1; it functions as an uptake transporter when tested in vitro at a pH of 7.4 or higher, while it extrudes its substrates at lower pH.
According to the ICH harmonization guideline, MATE1-mediated drug interactions should be assessed for new molecular entities (NMEs) that undergo significant renal elimination. Simultaneous evaluation of OCT interactions is also indicated.
PreadyTake OCT2 contains HEK293 cells genetically manipulated with the SLC22A2 gene to overexpress the organic cation transporter-2 (OCT2). Together with MATEs, it plays a key role in the disposition and renal clearance of mostly cationic drugs and endogenous compounds. Current guidances1 recommend evaluating OCT2-mediated drug interactions.
OCT2 is expressed in the basolateral (blood) side of the kidney’s proximal tubule cells. It works in conjunction with MATE1 to help eliminate OCT2 substrates through urine. The secretion of organic cations involves a two-step process: first, OCT2 transports these molecules from the blood into the renal proximal tubule, which initiates renal elimination. Next, the MATE transporter further secretes these compounds into the urine.
In addition to organic cations, OCT2 transports anionic and zwitterionic compounds. It also helps regulate the concentration of endogenous substances such as serotonin, acetylcholine, and histamine within the interstitial and intracellular spaces. Although OCT2 exhibits bidirectional movement when tested in vitro, it primarily functions as an uptake transporter at physiological pH (7.4).
According to the ICH harmonization guideline, compounds that undergo significant renal elimination should evaluate their OCT2 liabilities. Additionally, a simultaneous assessment of MATE interactions is advised.
PreadyTake OATP1B3 contains HEK293 cells transfected with the SLCO1B3 gene to overexpress the organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B3 (OATP1B3), a transporter involved in internalizing drugs to the liver for biliary excretion. This transporter, important for liver drug elimination, is recommended for investigation by regulatory guidelines.
OATP1B3 is almost exclusively expressed in the basolateral membrane of the hepatocytes located around the central vein (centrilobular hepatocytes). This transmembrane protein mediates the uptake of xenobiotic and endogenous compounds, playing a critical role in bile acid and bilirubin transport. OATP1B3 shares substrates and inhibitors with OATP1B1, another major hepatic uptake transporter.
OATP1B3 is seen as an uptake transporter, although there is evidence for bidirectional transport activity. Its deficiency results in bile acid accumulation (cholestasis) and, consequently, in liver injury.
According to the ICH harmonization guideline, drugs partially or predominantly eliminated by the liver are asked to predict drug interaction potential.
Our 96 multiwell insert plates with differentiated MATE1, OCT2 and OATP1B3-overexpressing HEK293 cells are relevant to study drug-transporter interaction according to regulatory recommendations.
Transporter-mediated drug interactions are assessed by comparing compound accumulation in cells overexpressing the transmembrane protein and nonspecific accumulation in those expressing the empty vector.
Dive deeper into transporters in our detailed article.
Read more
Fluorescently labelled molecules evaluate transporter activity post-shipment in those cells overexpressing the uptake transporters and their control counterparts. Sodium fluorescein is the substrate for the organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 (OATP1B3). Trans-4-[4-(Dimethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridinium iodide (trans-ASP+) is used to characterize transporter activity in those cells individually expressing the multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 (MATE1) and the organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2).
We provide fluorescently labelled reference compound uptake for each batch after shipment so the customer can have reference values for transporter activity.
No, the Shipping Medium consists of a semi-solid culture system specifically designed to preserve cells at room temperature (15-25ºC). This medium maintains a suitable physicochemical environment, keeping adequate moisture conditions for cellular homeostasis and forming a protective cushion that protects cell integrity and functionality during long-distance shipments up to seven days.
As a general rule, we act as a supplier and do not provide testing services. Nonetheless, feel free to contact us if you wish to test our plates externally. We can direct you to our partners who can assist you in conducting the assay effectively. Additionally, in certain situations, we are open to collaborating to try out new applications of interest to both of us.
In vitro studies to evaluate drug clearance by hepatic, biliary excretion, and renal active secretion should be considered if drug elimination is ≥25% of its systemic clearance. Organic Anion-Transporting Polypeptide (OATPs) are important hepatic uptake transporters. In contrast, Organic Cation Transporter OCT2 and renal efflux transporters (Multidrug and Toxin Extrusion Proteins (MATE1) are often involved in active renal secretion.
In addition to regional guidelines, the harmonized guideline for drug interaction studies provides recommendations for designing, conducting, and interpreting these assays.
Some drugs may be potential substrates and inhibitors of hepatic, biliary and renal transporters. For example, metformin and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium iodide (MPP+) serve as reference substrates for the Multidrug and Toxin Extrusion Protein 1 (MATE1) and the Organic Cation Transporter 2 (OCT2), respectively. At the same time, valsartan is a reference substrate for the Organic Anion-Transporting Polypeptide (OATP)1B3. Quinidine (MATE1), doxepin (OCT2) and cyclosporin (OATP1B3) are well-known inhibitors of these transporters.
Drugs that are substrates for drug clearance transporters typically exhibit uptake ratios above 2 when assessed using transport assays in cells expressing the transporter versus their control counterparts (MOCK cells). The uptake ratio value decreases by at least 50 % in the presence of an inhibitor.
Biotechnology company specialized in the development and commercialization of innovative solutions for the pharmaceutical industry and biomedical research.