An investigation led by the researcher Nicoló Milani was published in the prestigious analytical journal Lab on a Chip. Under the title Application of a gut–liver-on-a-chip device and mechanistic modelling to the quantitative in vitro pharmacokinetic study of mycophenolate mofetil, CacoGoblet was employed to investigate the permeability and the metabolism of the compound in a gut-liver-organ-on-a-chip (OoC) model.
Organ-on-a-chip: a continuously evolving model
Preclinical drug discovery and development traditionally rely on animal models, but these are often inadequate for accurately predicting human pharmacokinetics (PK). One of the biggest challenges in the field is identifying predictive models that can more effectively simulate human responses. Microphysiological systems (MPS), which consist of multiple interconnected organ-on-a-chip components, have emerged as powerful tools in this regard, offering a more accurate translation from in vitro to in vivo drug disposition, efficacy, and toxicity predictions. Roche’s study tested mycophenolate mofetil and its metabolites for quantitative evaluation and employed a combination of HT-29 and Caco-2 cells with intestinal-liver OoC.
Study on Mycophenolate Mofetil
In the study, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and its metabolites were evaluated using a gut-liver OoC system. By combining HT-29 and Caco-2 cells, the researchers were able to assess the pharmacokinetics of MMF and its two main metabolites in this advanced model. This approach provided new insights into prodrug research, especially where the interaction of intestinal and hepatic processes influences the drug’s pharmacokinetic profile.
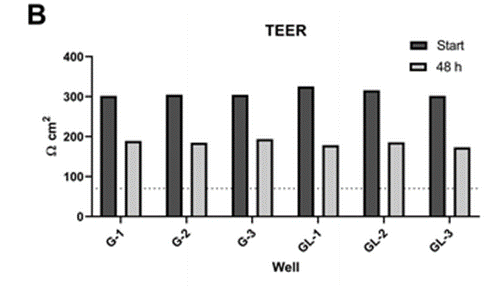
Experimental results
According to the study, the gut-liver OoC system allowed to study the pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil and its two main metabolites. This opened up the possibility for further research of prodrugs where a combination of intestinal and hepatic processes determine the drug and metabolite exposure. Furthermore, the team defined a robust and rigorous in silico modelling strategy which was fundamental for evaluation of the data from the combined gut–liver system. Finally, the demonstrated ability of the gut–liver OoC to capture the intestinal and liver metabolism of mycophenolate mofetil supports its potential for prediction of pharmacokinetics and drug–drug interaction risk of other orally administered drugs with complex in vivo behavior.
Read the full article: Milani N, Bruni G, Comi P, et al. Application of a gut–liver-on-a-chip device and mechanistic modelling to the quantitative in vitro pharmacokinetic study of mycophenolate mofetil. Lab Chip. 2024 Apr 10;24(7):1156-1167. doi: 10.1039/d4lc00167a. PMID: 37409112.