A study conducted by Nick Palmer from Astex Pharmaceuticals, researchers have made significant strides in identifying allosteric-binding site modulators for β-glucocerebrosidase (GBA/ GCase), an enzyme crucial for the treatment of Gaucher’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders.
The research, titled Fragment-Based Discovery of a Series of Allosteric-Binding Site Modulators of β‑Glucocerebrosidase, highlights the potential of fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) and incorporates permeability assays using CacoReady and PreadyPort plates.
What is GBA in Parkinson’s and Gaucher’s Disease?
GBA/ GCase is a lysosomal enzyme that plays a vital role in the hydrolysis of glucosylceramide, a lipid molecule. When GBA is dysfunctional, it leads to the accumulation of toxic substrates, contributing to the development of diseases such as Gaucher’s disease (GD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Mutations in the GBA gene can result in misfolded protein forms that disrupt cellular mechanisms, impairing enzyme function and leading to disease. Key therapeutic targets include:
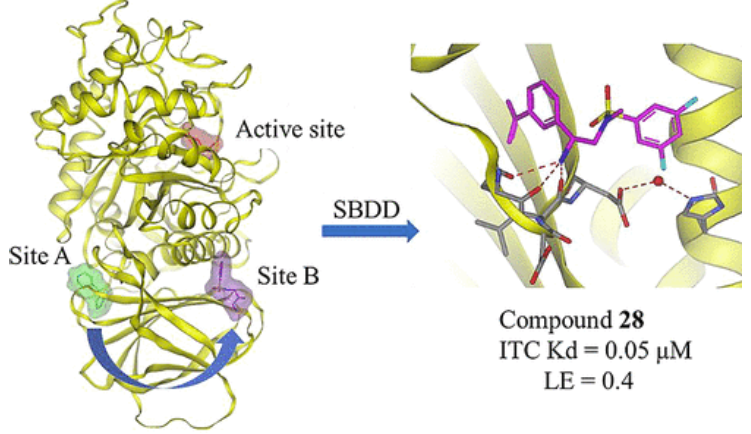
- Identification of Pharmacological Chaperones: Using fragment-based drug screening (FBDD) to identify compounds that act as pharmacological chaperones has the potential to stabilize misfolded forms of GCase and enhance its activity.
- Modulation of GCase Activity: Researchers aim to find compounds that not only bind to GCase but also positively modulate its activity under cellular conditions. This is crucial to improve the enzyme’s function in patients with mutations that cause its dysfunction.
- Development of Potential Therapies: The goal is to advance the development of new therapies that can be used to treat patients with diseases related to GCase dysfunction, such as Parkinson’s disease.
Utilizing CacoReady and PreadyPort
To evaluate the permeability and absorption characteristics of the newly discovered compounds, the researchers utilized CacoReady and PreadyPort ready-to-use plates:
- CacoReady: This system was crucial for assessing the permeability of compounds across a Caco-2 cell monolayer, a standard model for the intestinal barrier. The results indicated promising permeability, suggesting that these compounds could potentially be developed into effective oral therapeutics.
- PreadyPort: The PreadyPort-MDR1 system was used to explore the transport properties of the compounds, examining their ability to cross cell membranes and whether they are substrates for efflux transporters like P-glycoprotein.
Promising results
The study demonstrated that several compounds demonstrated a positive dose-dependent response in enhancing GCase activity in live cell assays. This finding is significant, as it suggests that these compounds could serve as effective treatments for patients with GCase-related disorders.
Read the article here: Palmer et al; “Fragment-Based Discovery of a Series of Allosteric-Binding Site Modulators of β-Glucocerebrosidase” J Med Chem, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00702